What to Build:Hospital Design & Construction.
The first step is to decide what type of hospital to be built. It can be a Multi-Speciality, super-specialty, single-specialty (eye, Cardiac) hospital. What size of the hospital, generally is described in bed strength: 50, 100, and 200 + beds. It is ideal to build a minimum 100-bed facility with a planned scope of expansion further to 200 – 400 beds.
Demand, Catchment, Service study: Understanding existing healthcare infrastructure and price points, will answer most of the questions in the first phase, and help to focus further in Operations and Marketing Strategy. Our Specialist Team for planning can work closely to do the survey and guide to make decisions based on data gathered on the field. Thumb rules to make decisions on the Investment required for a Hospital.
- Hospital Build size: 500 – 600 sq ft per bed. The smaller Capacity hospital will have a higher per-bed space requirement, as common departments like diagnostics Pharmacy, etc will be better utilized over larger bed strength.
- Cost of Construction: 3800 Rs per Sq Ft for a standard modern facility + Equipment cost.
Hospital Infra Requirements
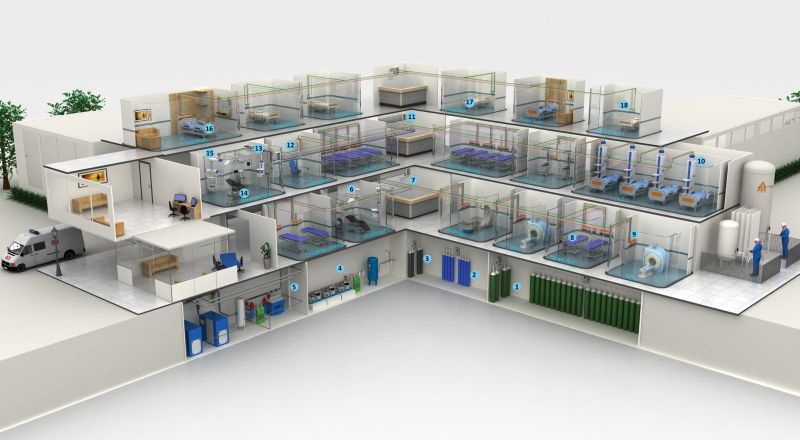
Hospitals are the most complex infrastructure. It requires a lot of different types of spaces as per the services you intend to provide. It is a 24 x 365 days working unit. Appropriate zoning is required keeping in mind infection control. Support service of Medical Gas, Suction, Diet, CSSD, Air, water, light is critical in providing a good patient experience.
Spaces that are to be planned in a hospital:-
- OPD: Consultation rooms, Registration Counter, Public Utilities (toiles, drinking water, Waiting Area, etc), Specialist OPD (eye, Ent), Procedure rooms (ortho, Dressing, etc).
- Radiology & Imaging: X-ray, CT scan, MRI, USG/ Colour Doppler
- Pathology: Phlebotomy, Microbiology, Histopathology, etc,
- Pharmacy: OPD Pharmacy, IPD Pharma, and Stores.
- Emergency: Ambulance receiving, Relatives waiting, triage, Minot OT, Observation beds, Duty doctor room, Nursing station, etc
- Daycare and Procedures: IVF, Dialysis, chemotherapy, Eye OT, Dental OPD, and Procedure.
- In-Patient: Wards, Private rooms, Semiprivate and Deluxe rooms, Nursing station, toiles, etc.
- Operation Theatre complex: Pre-Pot OP, Staff changing, Relatives waiting lounge, OT Consultation, CSSD, Operation theatre, Scrub, etc. Zoning to be ensured.
- Intensive care: ICU Beds, Nursing station, Doctor Duty room, Store, Relatives waiting, and consultation room.
- Neonatal Intensive Care, NICU: Level 3, TPN, Beds, NS, Duty Dr, Feeding rooms, Septic baby room, Nursery.
- Maternity: LDRP, Labour room, Nursery, and OT in the OT complex can be used for C sec.
- Cath Lab: control, Procedure Room.
- Oncology: PET CT, Linear accelerator Bunker, etc.
- Office: Accounts, HR, Insurance, SCM
- Stores: General, Bio-medical, Pharmacy, Maintenance
- Staff Areas: Changing, Dining
- Kitchen, Laundry
- Electrical Panel, UPS, Medical Gas & Vacuum room, Security and CCTV monitoring, Fire control room.
- Blood Bank: Component separation, Waiting Area, Registration Counter, Medical Examination, Donation Room, Refreshment room, Sterilisation cum washing, Store and Record, TDD, etc.
This list is not complete, based on the hospital size some of the spaces can be clubbed. Proper zoning and flow of man and material to be planned, to avoid chaos. Like emergency flow, flow is to be separated from OPD flow. Hospital Infra has to Focus on Patient Experience & Infection Control, Health infra is aspirational, and building and maintaining infrastructure increases patient experience. Hospital Façade (exterior looks) also plays an important role in patient aspirational needs. Along with treatment services, hospital infra helps build a strong brand image. We are the Best Hospital Turnkey Project Management Company.
Utilities are complex in a hospital. Eg. for Electricity we should provide 3 separate wirings, 1. Grid power, 2. Generator Backed Power 3. UPS Backed power. All these types are in series with 1 backing 2 and 2 to 3. As it becomes costly to have a 100 % backup of Grid power to DG and then to 100 % UPS, separate wiring and circuits are designed. But ideally, all can be back-to-back covers. For a 200-bed hospital, 750 kW of the grid, 250 kW of DG, and 150 kW of UPS should be sufficient. Higher power requirements lot depend on heavy machines like CT, MRI, and CATH lab.
A similar type of complexity is there in Water (DM for Dialysis, RO water, General water), Sewage lines going to STP and in some cases treatment and recirculating wastewater. Central Oxygen and Vacuum line provision for all the critical beds and OT. Solar Water heating system is mandatory in some states.
Fire Detection and Prevention: to be installed keeping National Building Code provision in Mind, this has the following components: Fire Hydrant System, Sprinkler System, UG Fire reservoir, OH Tank, Smoke detector, Fire alarm System, Public Address system, Fire Extinguishers.
Communication Systems: Telephone, LAN, CCTV, TV, and Public-Address Systems. Hospital Turnkey Project.
Air, Temperature, and humidity are controlled using either unitary Air Conditioners or central ducting systems. Air needs to be sterilized as this is a major cause of infection, so either HEPA filers to be put in central ducted AHU or Air cleaners/ Sterilisers to be installed. OTs should be provided with Laminar Airflow systems. Sufficient air changes are to be planned as the air conditioners recirculate internal air. 8 air changes per hour inward and 30 in OT are generally recommended.
Light, Sufficient natural light increases the feeling of well-being. The artificial light of 300 Lux is to be provided on all the working surfaces. LED lights decreased the total cost of ownership.